A journey of a thousand miles begins with a single step. As children grow, their feet may develop inversion, eversion, high arches, flat feet, etc. It is sometimes difficult to distinguish whether it is normal development or pathological conditions, which brings great trouble and doubts to parents. Insufficient knowledge or premature or excessive intervention will affect the normal physiological development of children.
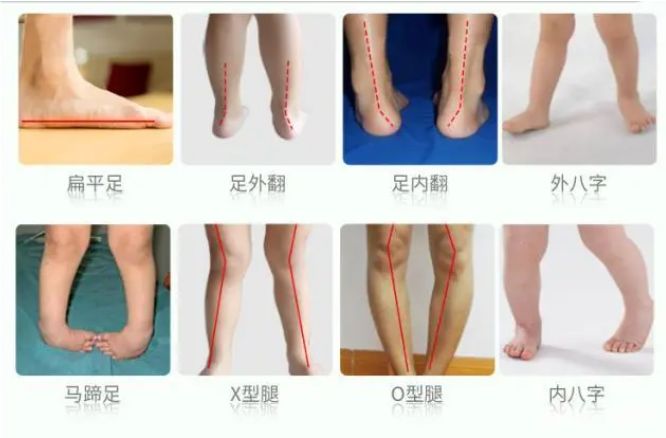
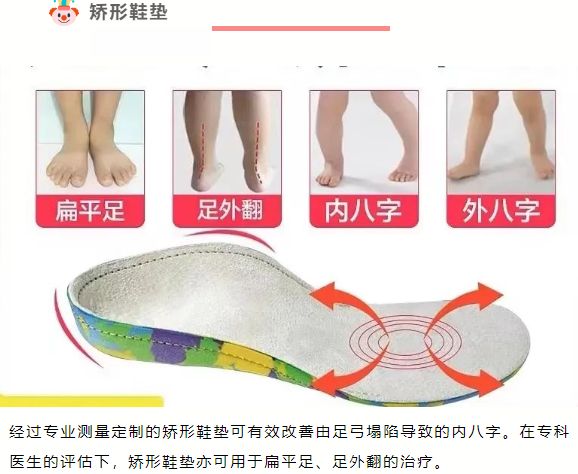
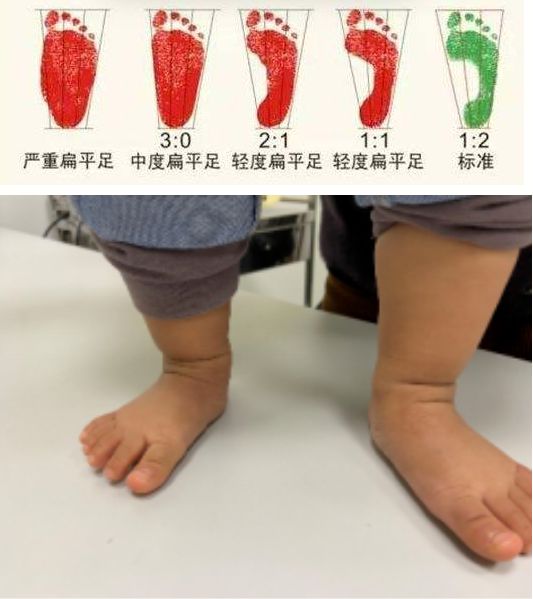
Refers to the loss of the normal medial longitudinal arch of the foot, also known as arch collapse. Most children have soft flat feet, so parents do not need to worry too much. Let the children exercise moderately, strengthen the training of the plantar flexors, control their weight, and do a good job of observation and follow-up. 0-4 years old: The medial longitudinal arch does not appear, showing physiological flat valgus feet. In addition to daily precautions, only good observation and follow-up are required. 4-10 years old: From the appearance of the medial longitudinal arch to maturity, if there are no clinical symptoms, only good observation and follow-up are required. However, if combined with symptoms such as Achilles tendon or gastrocnemius contracture, foot valgus, heel pain, etc., intervention treatment is required.
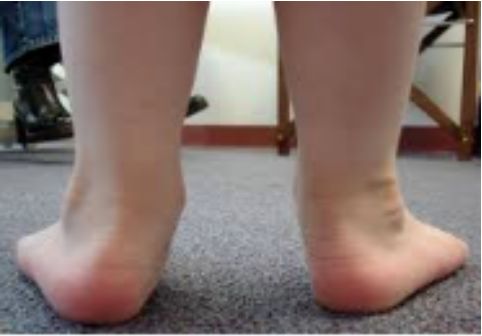
It is a common postural foot deformity and a congenital disease. It is characterized by dorsiflexion and eversion of the foot. Children's foot eversion often occurs together with flat feet, usually manifested as calcaneal eversion and excessive pronation of the subtalar joint. When standing and walking, it manifests as force on the inner side of the foot, which not only affects gait, but can also cause obvious deformity in severe cases.
Claw foot, also known as claw foot, is a common deformity characterized by a high longitudinal arch of the foot. A small number of cases are congenital, while most occur after the age of 3 and are caused by neurological diseases, such as tethered cord syndrome, syringomyelia, and hereditary neurological diseases.
Patients with high arches are prone to sprains and movement disorders. Some patients can be treated with foot orthotics, including the use of special insoles, while some patients with high arches require surgical treatment.
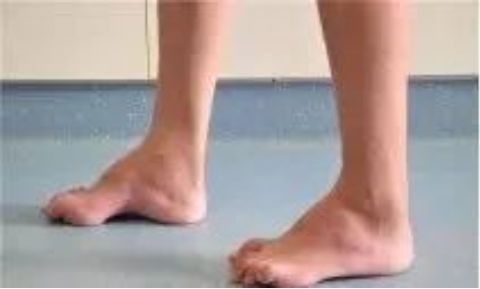
Every child has different foot and ankle problems. Some can be significantly improved through rehabilitation training, some need to wear orthopedic braces, and some need surgery or botulinum toxin injections. Therefore, a doctor's professional evaluation is needed to develop a suitable treatment plan. If your child has foot and ankle problems, please consult a doctor in time.